Opioid Overdose Prevention Programs Providing Naloxone to Laypersons — United States, 2014
(aside) Our little operation is on the list! We're that small dot on CA's Central Coast, mid way between LA and SF -
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6423a2.htm?s_cid=mm6423a2_e
Opioid Overdose Prevention Programs Providing Naloxone to Laypersons — United States, 2014
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), June 19, 2015
Eliza Wheeler, MPA1; T. Stephen Jones, MD2; Michael K. Gilbert, MPH3; Peter J. Davidson, PhD4 (Author affiliations at end of text)
Drug overdose deaths in the United States have more than doubled since 1999 (1). During 2013, 43,982 drug overdose deaths (unintentional, intentional [suicide or homicide], or undetermined intent) were reported (1). Among these, 16,235 (37%) were associated with prescription opioid analgesics (e.g., oxycodone and hydrocodone) and 8,257 (19%) with heroin (2). For many years, community-based programs have offered opioid overdose prevention services to laypersons who might witness an overdose, including persons who use drugs, their families and friends, and service providers. Since 1996, an increasing number of programs provide laypersons with training and kits containing the opioid antagonist naloxone hydrochloride (naloxone) to reverse the potentially fatal respiratory depression caused by heroin and other opioids (3). In July 2014, the Harm Reduction Coalition (HRC), a national advocacy and capacity-building organization, surveyed 140 managers of organizations in the United States known to provide naloxone kits to laypersons. Managers at 136 organizations completed the survey, reporting on the amount of naloxone distributed, overdose reversals by bystanders, and other program data for 644 sites that were providing naloxone kits to laypersons as of June 2014. From 1996 through June 2014, surveyed organizations provided naloxone kits to 152,283 laypersons and received reports of 26,463 overdose reversals. Providing opioid overdose training and naloxone kits to laypersons who might witness an opioid overdose can help reduce opioid overdose mortality.
Since 2008, HRC has maintained a database of organizations providing naloxone kits to laypersons. The Opioid Safety and Naloxone Network is a national network of naloxone experts, program administrators, and advocates. Before the survey, HRC staff polled network participants for information on any new organizations providing naloxone kits to laypersons that should be included in the survey. In July 2014, HRC e-mailed a link to an online survey to managers of 140 organizations known to provide naloxone kits to laypersons. These organizations included public health departments, pharmacies, health care facilities, substance use treatment facilities, and community-based organizations providing services to persons who use drugs, including current or former opioid (heroin or pharmaceutical) users, and other potential witnesses to overdoses. Law enforcement organizations, emergency medical services, and other professional first responders using naloxone were not included in this survey.
The survey included questions about the year the organization began operating; the numbers of sites or local programs providing naloxone kits; the number of persons trained in overdose prevention and provided naloxone kits; and the number of reports of overdose reversals (administration of naloxone by a trained layperson in the event of an overdose) (4), as well as whether the reports were based on program data or were estimates. The survey also asked about the naloxone formulations currently provided in kits, models for training and providing naloxone kits, funding sources, and any difficulties obtaining naloxone. To obtain data for a recent full calendar year, organizations providing naloxone kits during calendar year 2013 were asked to provide specific data for that year, including numbers of persons provided naloxone kits, reversals reported, and naloxone vials provided; characteristics of persons who received naloxone kits (e.g., persons who use drugs, friends and family members, service providers); characteristics of persons reporting overdose reversals; and the drugs involved in reported overdose reversals. HRC staff used follow-up e-mails and telephone calls to encourage participation and clarify responses.
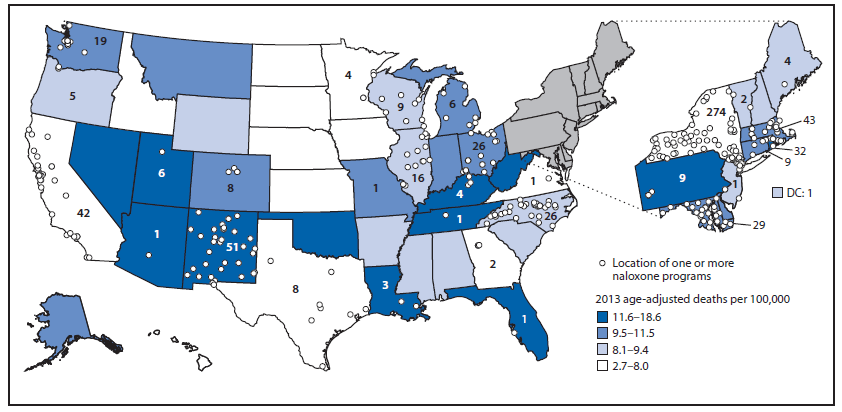
Managers from 136 (97.1%) organizations completed the survey, including those from 84 community-based organizations, 18 health care facilities, 10 Veterans Administration health care systems, 18 state or local health departments, and six pharmacies. Half of the responding organizations began operating during January 2013‒June 2014 (Figure 1). Respondents provided reports for 644 local opioid overdose prevention sites that provide naloxone kits, located in 30 states and the District of Columbia (DC) (Figure 2). Thirty-eight respondents provided consolidated data for multiple local sites providing naloxone kits. Some organizations estimated responses; for example, one health department estimated the number of laypersons receiving naloxone kits on the basis of the number of kits distributed to local sites. Three state health departments (Massachusetts, New Mexico, and New York) oversee operations of statewide naloxone programs, with 334 local sites (51.9% of the 644 local sites).
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6423a2.htm?s_cid=mm6423a2_e
![]()
![]()